All about Kidney Pain: Location, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Introduction
Kidneys are vital organs that play numerous regulatory roles in humans and animals. They are of great importance in the urinary system. They excrete waste products in urine and are the body's natural filter of the blood. Kidneys filter and detoxify our body effectively. If toxins are not properly excreted out, they can poison our body resulting in diseases.
Kidney pain is often related to infection or an injury to the kidney. When kidneys are malfunctioning or infected, then kidney pain can be severe. Kidney pain may be related to injury: accident or falling down with pressure may damage the kidneys. Although kidney pain is closely related to back pain, kidney pain and back pain may have totally different causes. Back pain symptoms may be caused by kidney infections and vice versa. For help differentiating kidney pain from back pain, see http://www.diffen.com/difference/Back_Pain_vs_Kidney_Pain.
Kidney pain is often related to infection or an injury to the kidney. When kidneys are malfunctioning or infected, then kidney pain can be severe. Kidney pain may be related to injury: accident or falling down with pressure may damage the kidneys. Although kidney pain is closely related to back pain, kidney pain and back pain may have totally different causes. Back pain symptoms may be caused by kidney infections and vice versa. For help differentiating kidney pain from back pain, see http://www.diffen.com/difference/Back_Pain_vs_Kidney_Pain.
Location of the Kidneys
Kidneys are located underneath the diaphragm on either side of the spine above the gluteal region. If the pain in the kidney is stabbing or severe, it may extend to the back of the body.
For further reading: Kidney pain location
Location of the Kidneys
sss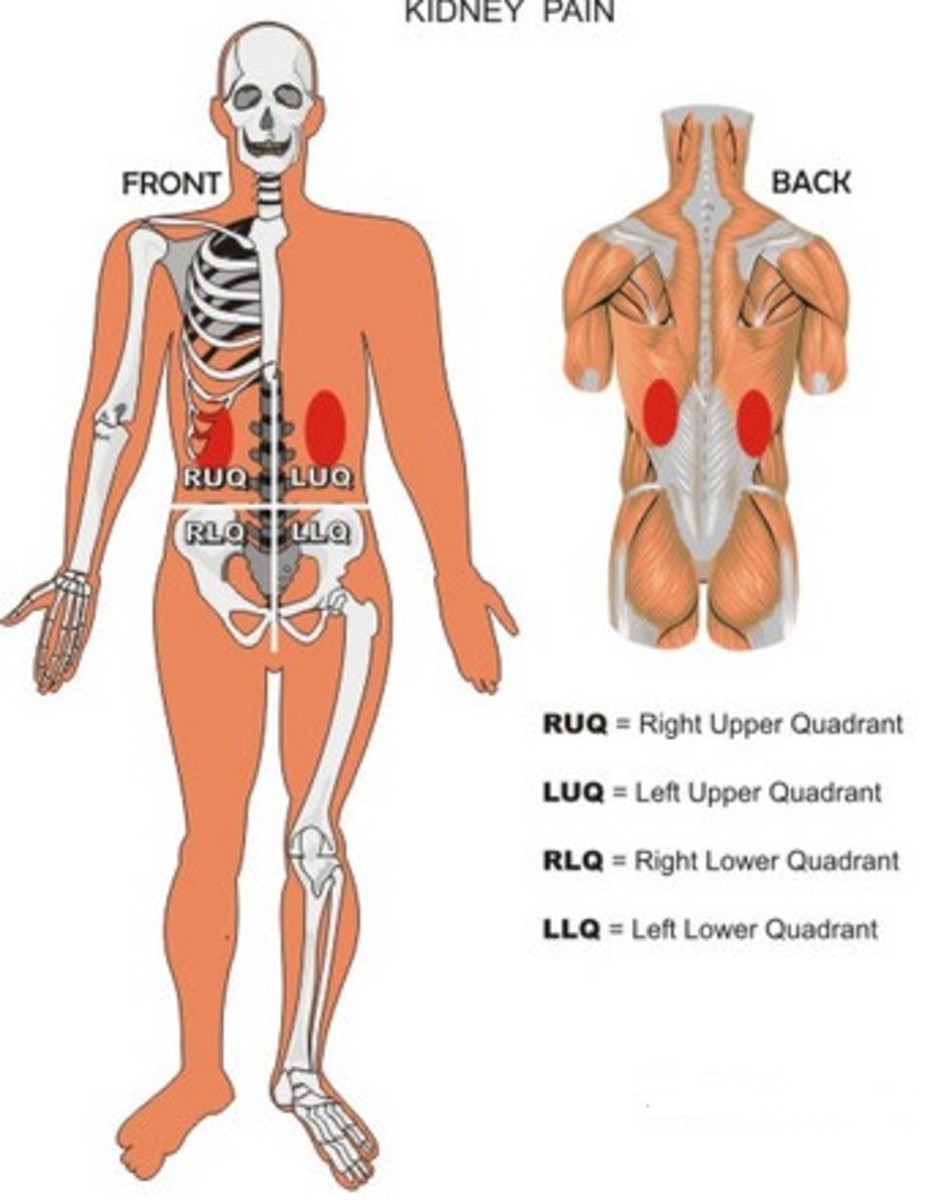

Kidney Pain and its Characteristics

Source
Causes of Kidney Pain
There can be many causes of pain in the area of the kidneys, including normal muscle sprain (connected to the back) or flank pain (between the bottom of the rib and the buttock). A person suffering from any of the below-mentioned abnormalities may be a prey to kidney pain.
Kidney stones. Kidney pain is caused when a stone develops or a blockade occurs in the ureter (a thin tube that connects kidney with the bladder). When urine flow is blocked or hampered, urine may collect in the kidney. Pain due to kidney stones is referred to as "colic," which means wave-like pain, different from a constant steady pain. It is very difficult for patients with renal colic to hold still while pacing and writhing. Patients experience nausea and vomiting when such pain is very severe.
Kidney infection. A kidney will get infected when kidney stones are incapable of getting flushed out. The kidney swells and stretches, and pain is felt in the sensitive area.
Arteriosclerosis. This happens when arterial walls are occupied by fatty material. Fats block the blood flow causing arteries to harden. Drug therapy may help in decreasing the causes of arteriosclerosis.
Kidney cancer. When kidney infection gets severe and bacterial infestation has spread out, the kidney capsule is stretched and the pain is at high-pitch.
Polycystic kidney. Enlargement of the kidney accelerates kidney pain. This disease is believed to be hereditary. Pain is more likely to be felt in the front of the abdominal region instead of in the lower ribs or back.
Urinary tract infection. The urinary system is made up of the bladder, kidney, ureter and urethra. Urinary tract infection usually takes place when kidney stones are developed.
Kidney infection. A kidney will get infected when kidney stones are incapable of getting flushed out. The kidney swells and stretches, and pain is felt in the sensitive area.
Arteriosclerosis. This happens when arterial walls are occupied by fatty material. Fats block the blood flow causing arteries to harden. Drug therapy may help in decreasing the causes of arteriosclerosis.
Kidney cancer. When kidney infection gets severe and bacterial infestation has spread out, the kidney capsule is stretched and the pain is at high-pitch.
Polycystic kidney. Enlargement of the kidney accelerates kidney pain. This disease is believed to be hereditary. Pain is more likely to be felt in the front of the abdominal region instead of in the lower ribs or back.
Urinary tract infection. The urinary system is made up of the bladder, kidney, ureter and urethra. Urinary tract infection usually takes place when kidney stones are developed.
Associated Symptoms of Kidney Pain
When the following symptoms are experienced, then there's valid ground to believe that pain being experienced is related to the kidneys.
- While urinating, abnormal color is detected. For example, blood.
- When piercing back pain is felt in the middle region, below the rib cage, or in the groin region.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- When urination becomes painful and is associated with an excessive unpleasant smell.
- When women undergo painful menstruation followed by fever, loss of appetite, extreme weight loss, and extreme pain in the lower abdomen.
- Noticeable colored swelling of hands, face, or feet, or abnormality in the nails, followed by fatigue and abnormal blood pressure.
Differential Diagnosis of Kidney Pain
Self-diagnosis of kidney-related pain is not recommended as it is very risky. Whenever the above-mentioned symptoms are found in a patient, instead of self-doctoring or self-medication, a proper doctor should be consulted. A doctor will check the overall condition of the patient, for example, the blood pressure, heart rate, respiratory rate, and temperature, in order to examine the overall state of health.
Physicians will also check for the signs and symptoms of any kidney-related disorder. A physical examination and a urine test will be conducted. The urine test will determine if the patient has any history of urinary tract infection. A physician will check the middle or lower part of the patient's back to find out any sensitive area related to tenderness or pain. Overall, the physician will suggest you alternative procedures for your next examination.
Physicians will also check for the signs and symptoms of any kidney-related disorder. A physical examination and a urine test will be conducted. The urine test will determine if the patient has any history of urinary tract infection. A physician will check the middle or lower part of the patient's back to find out any sensitive area related to tenderness or pain. Overall, the physician will suggest you alternative procedures for your next examination.
Treatment of Kidney Pain
Depending on the severity of kidney pain, precautionary measures should be taken.
- Consumption of over ten glasses of water per day should be made mandatory for the patient. Drinking more water causes more fluid to pass through the urinary tract, thus flushing out harmful bacteria. Drinking water is good for prevention of painful kidney stones.
- Better eating habits including more intake of vegetables and liquids should be encouraged, along with oranges, watermelons, grapes, cranberries and other juicy fruits. Cranberry has antibiotic properties which prevent harmful micro-organisms from attacking the body. Cranberries can also be consumed as supplements in the form of tablets, capsules, or fresh or dried powder.
- The patient should take vitamin C in addition to the diet program, which will help strengthen the body and avoid kidney complications.
- Intake of carbonated drinks, coffee, sodas and other acidic drinks should be discouraged. Most of these ingredients have harmful substances that may cause hardening of the kidneys and can increase the chances of kidney stone formation.
- If you wish to take antibiotics with your regular pain killer, get your physician to prescribe them. You may never know when your kidney has been infected and left untreated which can implicate your health issues. It is, therefore, important that to get the right treatment from your physician.


















No comments